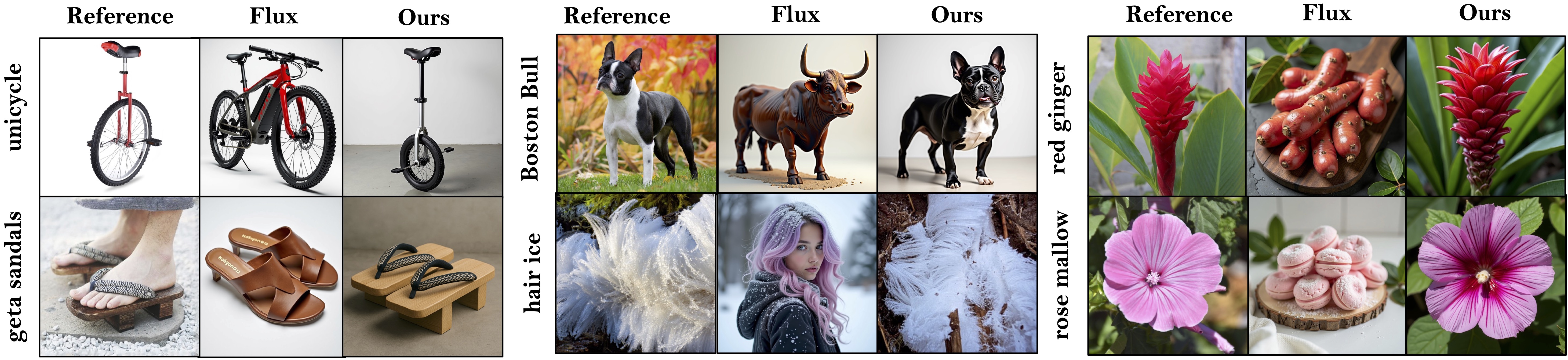
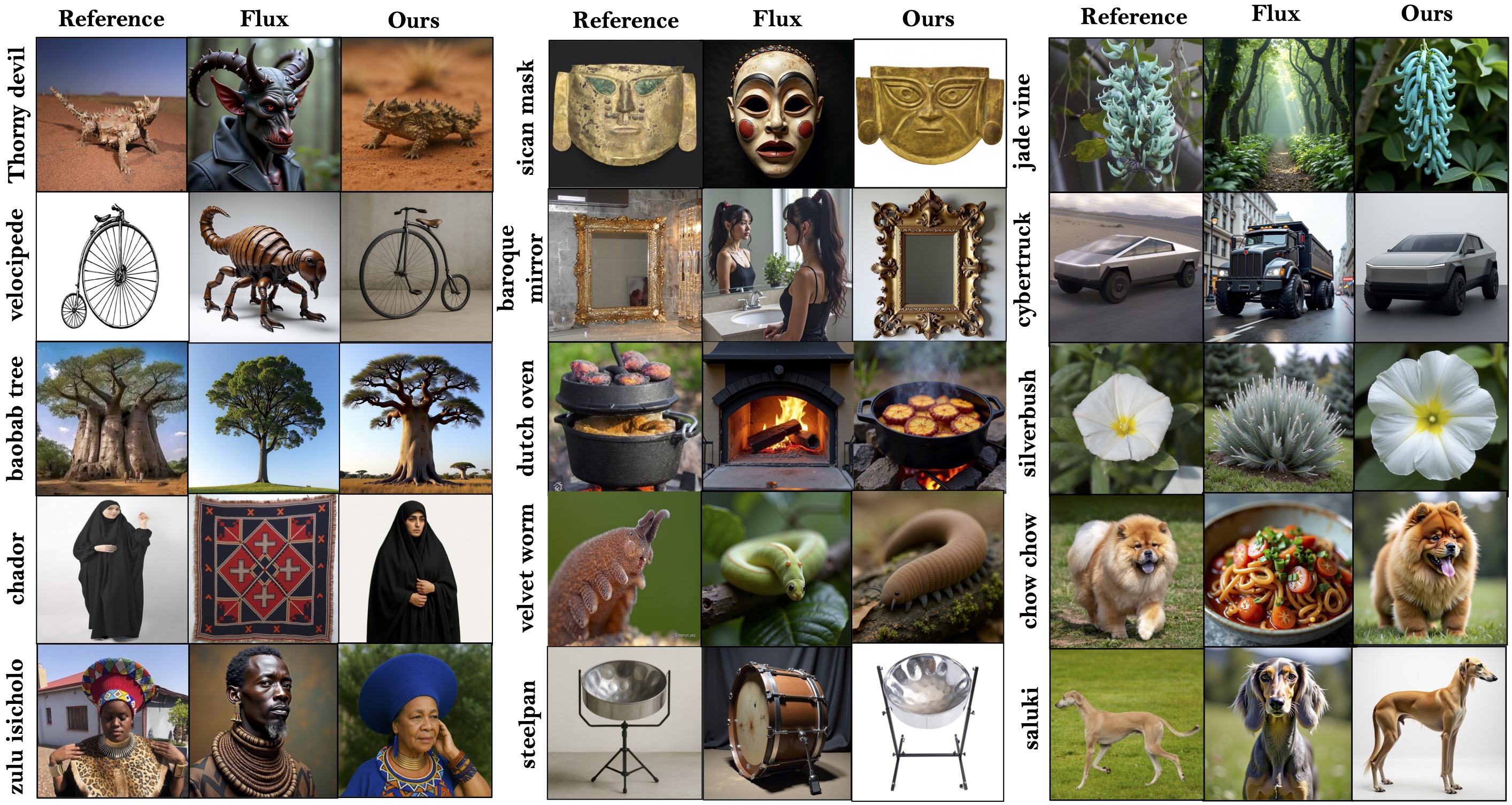
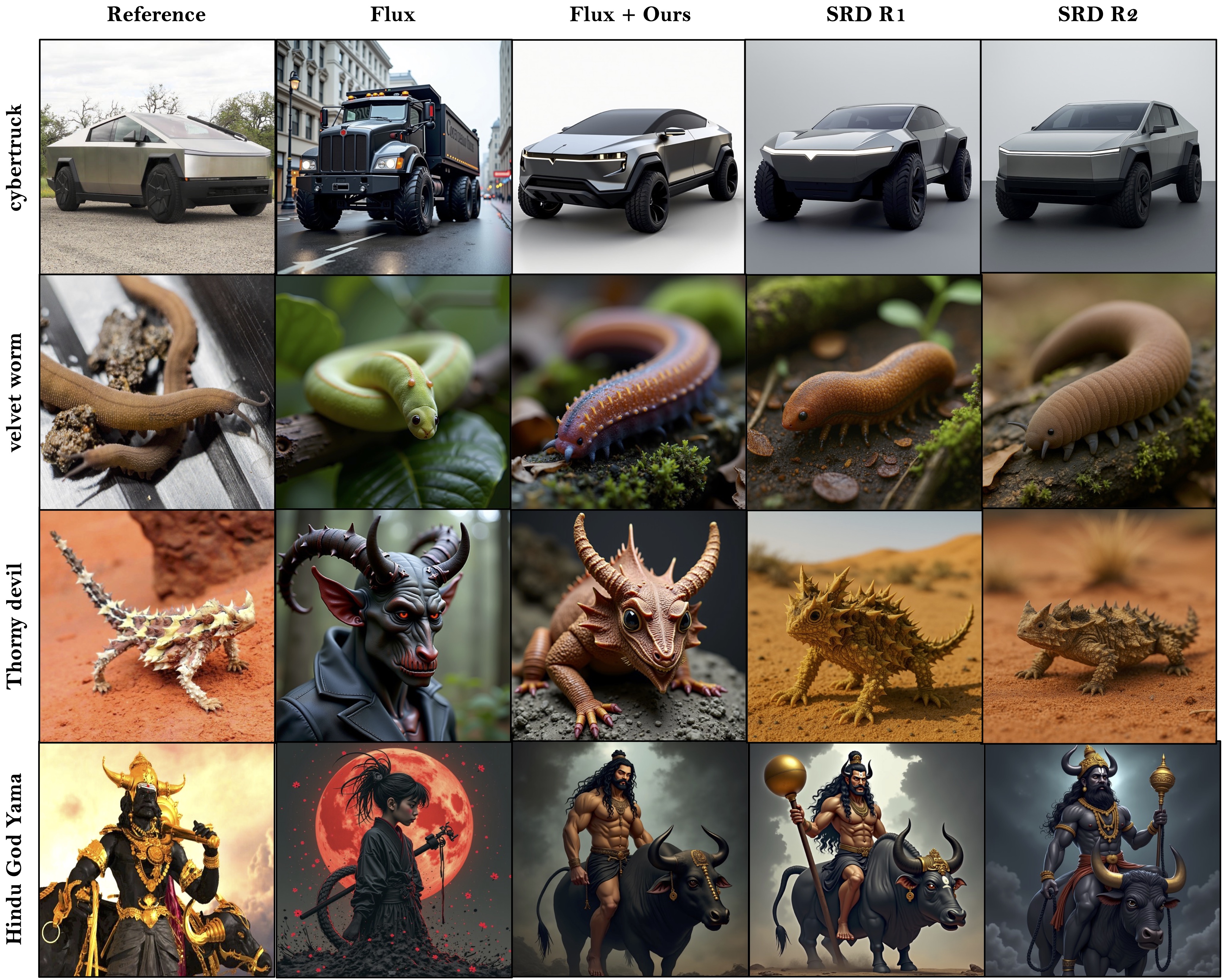
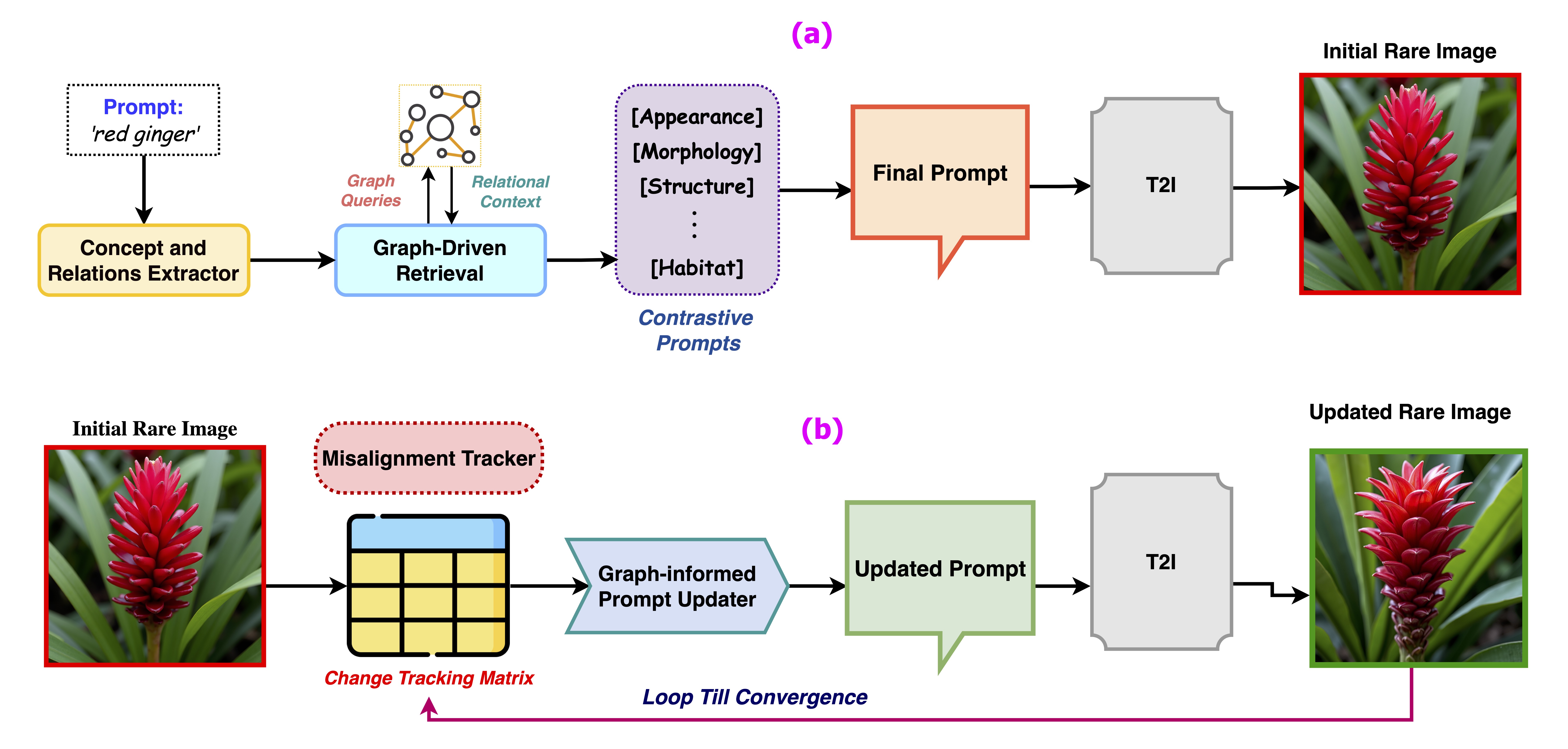
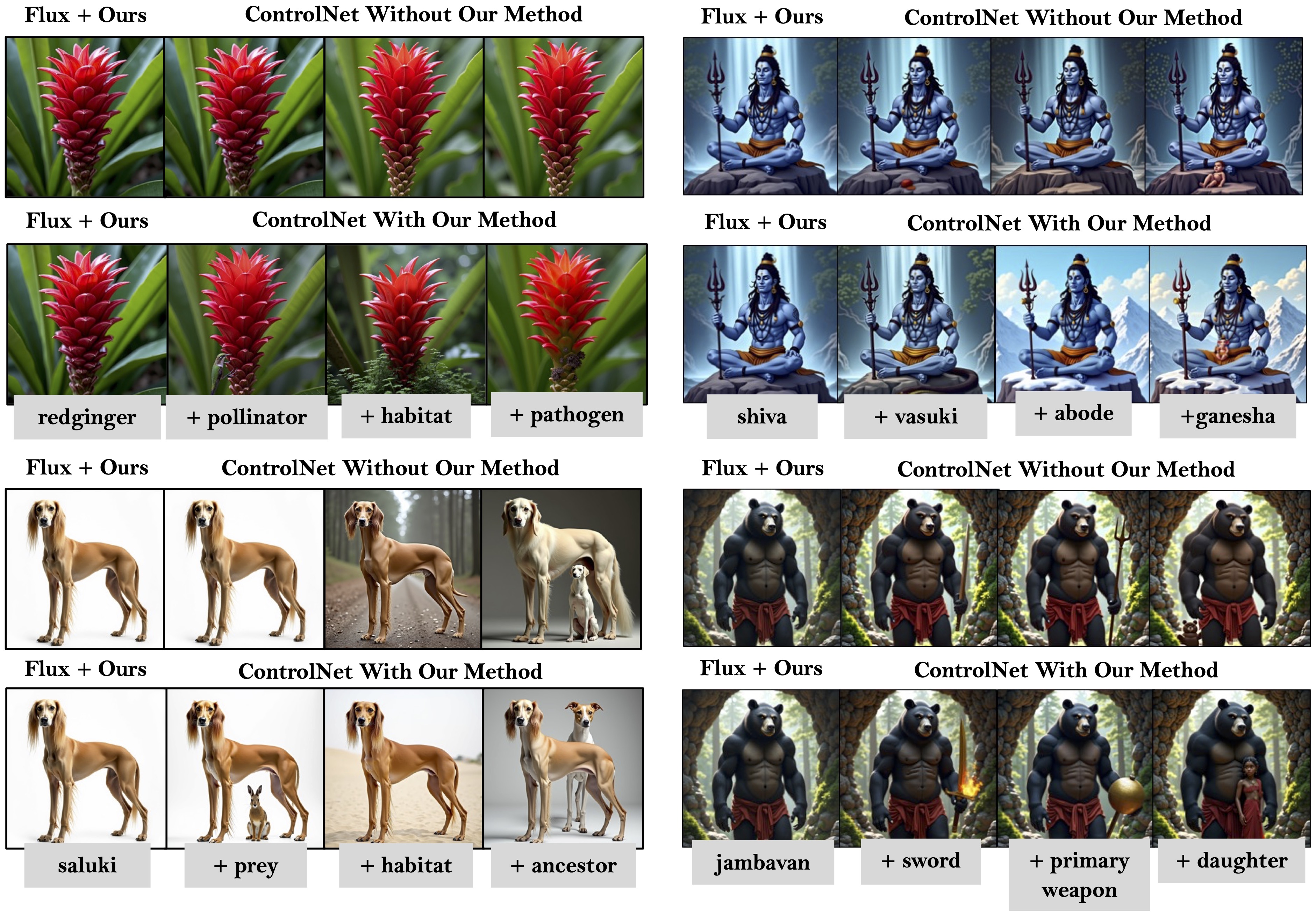
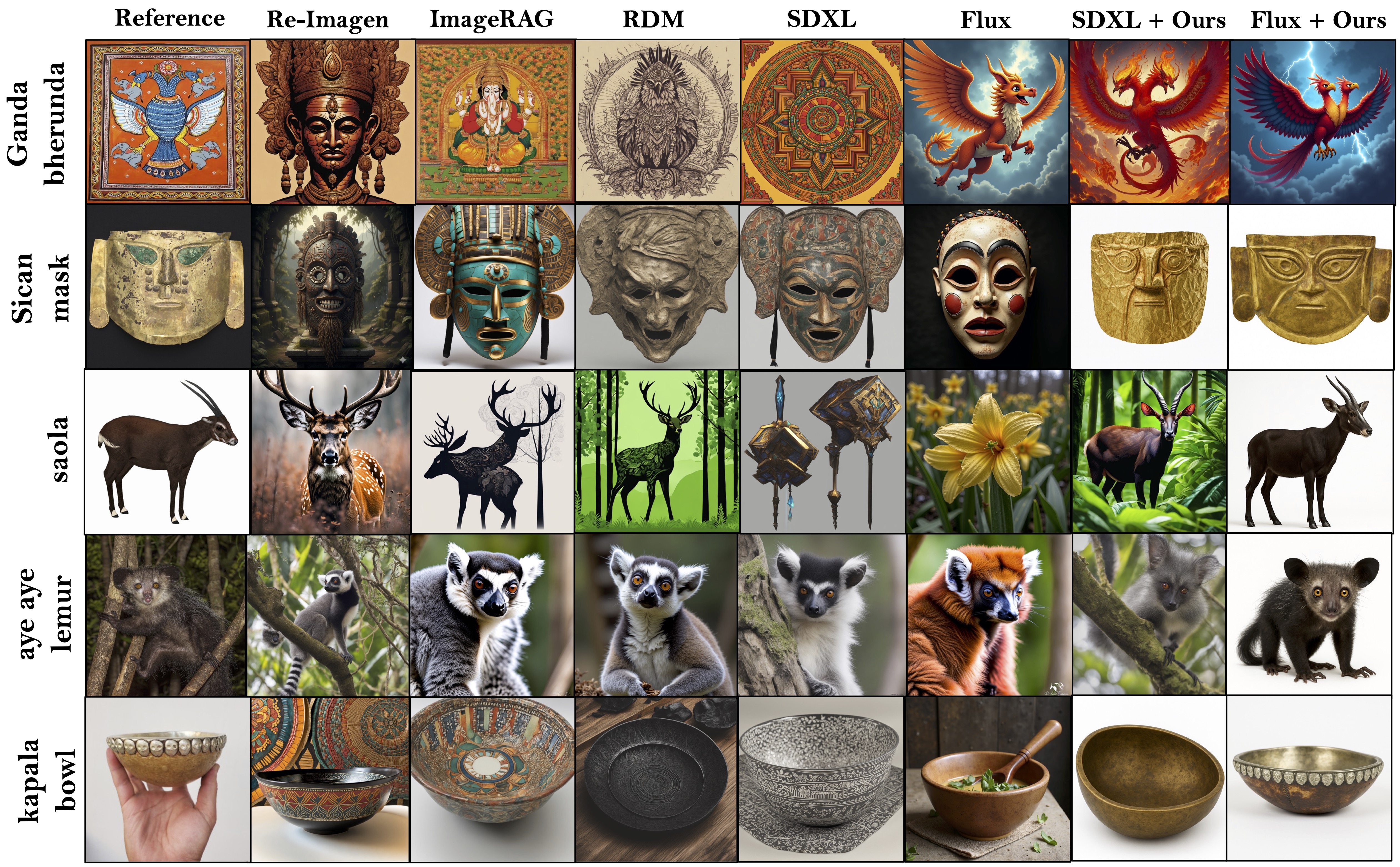
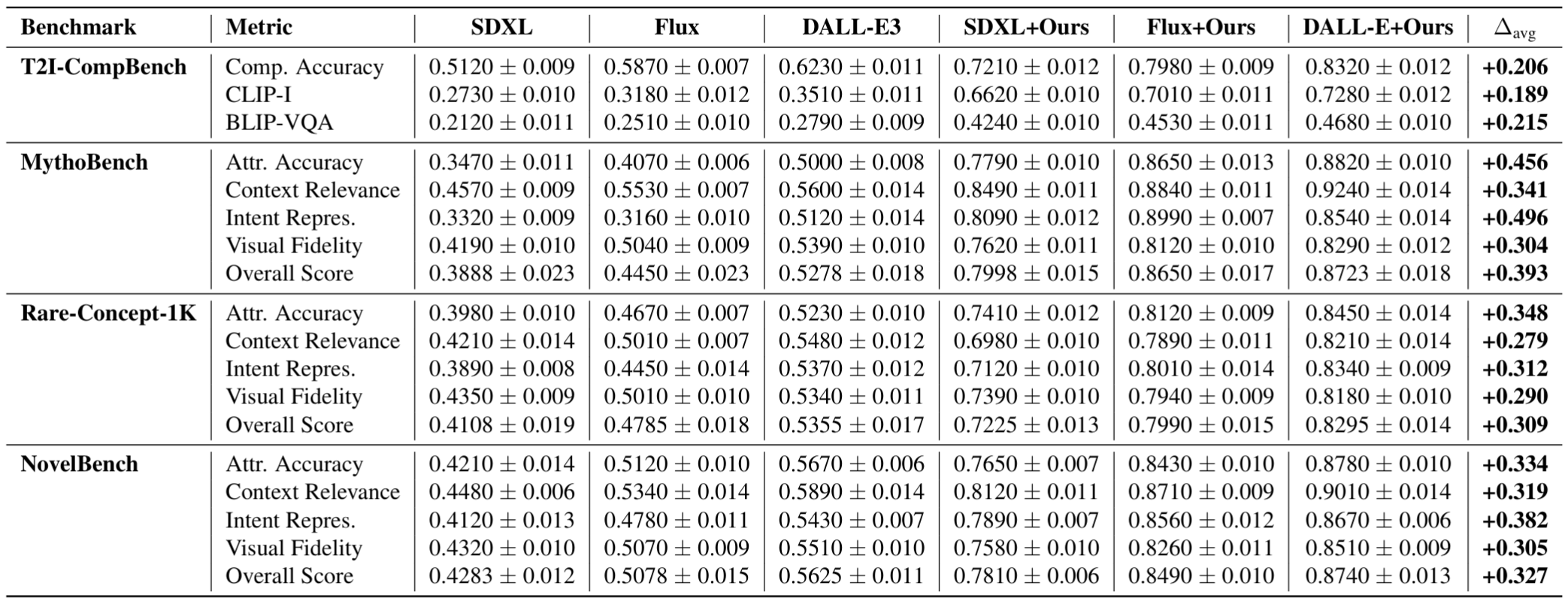
Despite impressive visual fidelity, current text-to-image (T2I) diffusion models struggle to depict rare, complex,
or culturally nuanced concepts due to training data limitations. We introduce RAVEL,
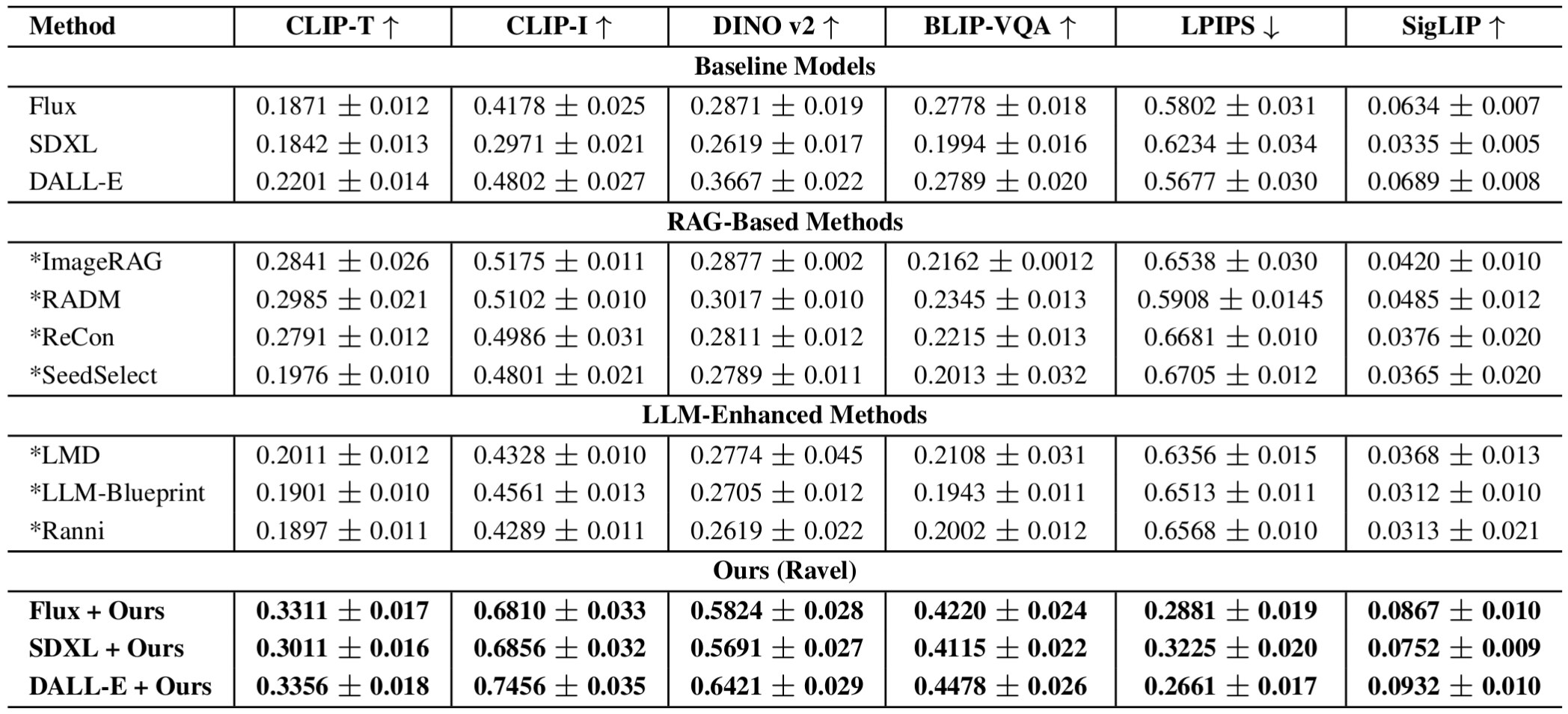
a training-free framework that significantly improves rare concept generation, context-driven image editing,
and self-correction by integrating graph-based retrieval-augmented generation (RAG) into diffusion pipelines.
Unlike prior RAG and LLM-enhanced methods reliant on visual exemplars, static captions or pretrained knowledge of models,
RAVEL leverages structured knowledge graphs to retrieve compositional, symbolic, and relational context,
enabling nuanced grounding even in the absence of visual priors. To further refine generation quality, we propose SRD,
a novel self-correction module that iteratively updates prompts via multi-aspect alignment feedback, enhancing attribute accuracy,
narrative coherence, and semantic fidelity. Our framework is model-agnostic and compatible with leading diffusion models including Stable Diffusion XL,
Flux, and DALL-E 3. We conduct extensive evaluations across three newly proposed benchmarks - MythoBench,
Rare-Concept-1K, and NovelBench. RAVEL also consistently
outperforms SOTA methods across perceptual, alignment, and LLM-as-a-Judge metrics. These results position RAVEL
as a robust paradigm for controllable and interpretable T2I generation in long-tail domains.